HEALTH
How Periodontal Therapy Prepares Patients For Orthodontics
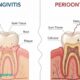
Healthy gums must come first. Orthodontic treatment on weak or infected gums can cause pain, loose teeth, and long recovery. That is why periodontal therapy comes before braces or aligners. It cleans deep around your teeth, removes hidden plaque, and calms swollen tissue. Then your mouth can handle the pressure of tooth movement. You breathe easier. You chew with less strain. You also lower your risk of future tooth loss. An orthodontist in Naperville will look at your gums before placing any brackets or trays. If there is bleeding, bone loss, or bad odor, you will likely need periodontal care. This step can feel slow when you want straight teeth now. Yet it protects your smile, your time, and your money. You deserve treatment that does not just move teeth. It should build a stable, strong mouth that lasts.
Why Gum Health Matters Before Braces
Teeth do not stand alone. They sit in bone and gum tissue. When this support breaks down, teeth shift, loosen, and hurt.
Gum infection, called periodontal disease, is common. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that almost half of adults over 30 show signs of it.
You might notice:
- Red or puffy gums
- Bleeding when you brush or floss
- Bad breath that does not go away
Braces or aligners put steady force on teeth. Without strong gums, that force can speed up damage. You may lose bone, feel loose teeth, and need more dental work later.
What Periodontal Therapy Does For You
Periodontal therapy is a set of treatments that clean below the gumline and help your body heal.
Common steps include:
- Deep cleaning of tooth roots
- Removal of plaque and hardened tartar
- Smoothing root surfaces so bacteria cling less
Sometimes your dentist may add medicine in the pockets around teeth. In some cases, surgery can reshape gums or bone. The National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research explains gum treatment options here NIDCR Gum Disease Treatment.
After treatment, you often see three changes. Your gums bleed less. Your breath smells cleaner. Your teeth feel steadier when you bite.
How Healthy Gums Support Orthodontic Treatment
You want straight teeth that last. Healthy gums give that chance. They help in three clear ways.
- Stronger support. Clean roots and healthy bones hold teeth steady while they move.
- Lower risk of tooth loss. Infection weakens bone. Treating it first cuts that risk.
- Better comfort. Less swelling means less soreness when braces start to move teeth.
Orthodontic force then works with your body, not against it. Movement becomes more controlled. Results remain more stable after treatment ends.
Comparing Outcomes With And Without Periodontal Therapy
This simple table shows how untreated gum disease can change your orthodontic journey compared to treated gums.
| Factor | Untreated Gum Disease | After Periodontal Therapy
|
|---|---|---|
| Gum health | Red, swollen, bleeding | Firm, less bleeding |
| Bone support | Ongoing loss and shrinkage | Stabilized with slower loss |
| Tooth stability | Higher risk of loose teeth | Teeth feel more secure |
| Orthodontic comfort | More soreness and pressure pain | More controlled and tolerable |
| Treatment time | More delays and extra visits | Fewer setbacks and smoother progress |
| Long term results | Higher chance of shifting and tooth loss | Better chance of stable, lasting alignment |
What To Expect Before You Start Braces Or Aligners
Your care team will walk through three main steps before orthodontic treatment.
- Gum and bone check. The dentist or periodontist measures gum pockets, checks for bleeding, and reviews X rays.
- Periodontal treatment plan. You may need deep cleanings, follow-up cleanings, and brushing and flossing changes at home.
- Healing time. Your gums need time to calm. You return for a recheck. If pockets shrink and bleeding drops, you are closer to braces.
This process may feel slow. Yet it protects you from sudden pain and emergency care during orthodontic treatment.
How You Can Support Healing At Home
Your daily habits matter as much as office treatment. You can protect your gums with three steady steps.
- Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
- Clean between teeth with floss or a small brush
- Keep regular dental visits for cleanings and checks
If you smoke, quitting helps your gums heal and hold teeth in place. Limiting sugary drinks and snacks also lowers plaque growth.
Working As A Team For A Safe, Straight Smile
You, your dentist, your periodontist, and your orthodontist form one team. Each brings a different skill. You bring daily care and honest answers about your habits. Your providers bring training and clear guidance.
When you treat gum disease before orthodontics, you reduce fear and surprise. You gain a cleaner mouth, stronger support, and a higher chance of keeping your straight smile for many years.
HEALTH
gingivitis vs periodontitis: What’s the Real Difference and Why It Matters

If you’ve ever noticed bleeding gums while brushing, you’ve probably paused and wondered:
Is this just mild gingivitis… or something more serious like periodontitis?
Understanding gingivitis vs periodontitis isn’t just helpful it’s essential. Both conditions affect your gums, but they are not the same. In fact, knowing the difference early could protect you from long-term tooth loss and expensive dental treatments.
In this comprehensive, SEO-optimized and easy-to-read guide, we’ll walk through:
-
What gingivitis really is
-
What periodontitis means for your oral health
-
The key differences between gingivitis vs periodontitis
-
Causes and risk factors
-
Symptoms to watch closely
-
The stages of gum disease
-
Treatment options
-
Prevention strategies
-
Frequently asked questions
Let’s break it down clearly, practically, and without unnecessary medical jargon.
What Is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is the earliest and mildest stage of gum disease. It happens when plaque — a sticky film of bacteria — builds up along the gumline and irritates the surrounding tissue.
Plaque forms naturally on your teeth every day. If it isn’t removed through brushing and flossing, it can inflame the gums.
Common Signs of Gingivitis
-
Red or swollen gums
-
Bleeding when brushing or flossing
-
Tender gum tissue
-
Mild, persistent bad breath
-
Slight gum sensitivity
Here’s the good news: gingivitis is reversible.
With proper oral hygiene and professional dental cleaning, your gums can return to a healthy state. There is no permanent bone damage at this stage.
That’s why early detection is so important.
What Is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is an advanced form of gum disease that develops when gingivitis is left untreated. Instead of staying limited to the surface gums, the infection spreads deeper into the supporting structures of the teeth.
This includes:
-
Connective tissue
-
Periodontal ligaments
-
Jawbone
Unlike gingivitis, periodontitis can cause permanent damage.
Symptoms of Periodontitis
-
Persistent bad breath
-
Gum recession (gums pulling away from teeth)
-
Deep pockets between teeth and gums
-
Loose or shifting teeth
-
Pain when chewing
-
Bone loss visible on X-rays
-
Pus between gums and teeth (in severe cases)
Periodontitis cannot be completely reversed, but it can be managed and stabilized with professional treatment.
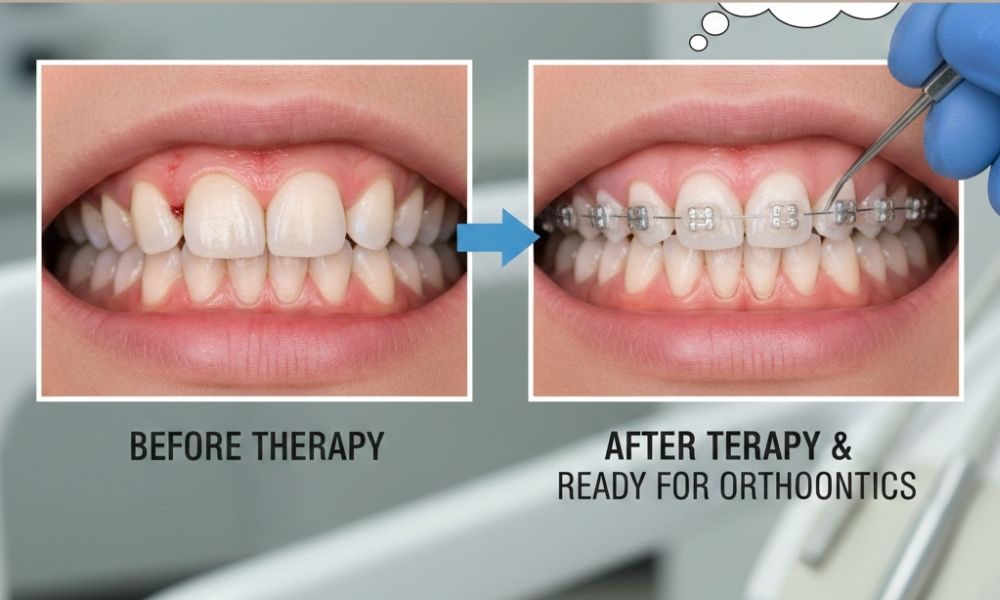
Gingivitis vs Periodontitis: The Core Differences
Understanding gingivitis vs periodontitis becomes easier when comparing them side by side.
| Feature | Gingivitis | Periodontitis |
|---|---|---|
| Severity | Mild | Advanced |
| Reversible | Yes | No (damage is permanent) |
| Bone Loss | No | Yes |
| Gum Recession | Rare | Common |
| Tooth Mobility | No | Possible |
| Risk of Tooth Loss | Low | High |
| Treatment | Cleaning & improved hygiene | Deep cleaning, possible surgery |
The Biggest Difference?
Gingivitis affects only the gums.
Periodontitis affects the gums, connective tissue, and bone.
That difference is critical.
What Causes Gingivitis and Periodontitis?
The main cause of both conditions is plaque buildup.
Here’s how it progresses:
-
Plaque forms on teeth.
-
It hardens into tartar (calculus).
-
Bacteria multiply under the gumline.
-
The body responds with inflammation.
-
Tissue breakdown begins.
If untreated, the inflammation extends deeper and begins destroying supporting bone which marks the transition from gingivitis to periodontitis.
Major Risk Factors
While plaque is the primary trigger, certain factors increase the likelihood of developing gum disease:
-
Poor oral hygiene
-
Smoking or tobacco use
-
Diabetes
-
Hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause)
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Chronic stress
-
Certain medications that reduce saliva
-
Poor nutrition
Smoking, in particular, significantly increases the risk of severe periodontitis.
Gingivitis vs Periodontitis Symptoms: How to Tell the Difference
Many people search for “gingivitis vs periodontitis symptoms” because early signs can overlap.
Signs You Likely Have Gingivitis
-
Bleeding while brushing
-
Puffy or swollen gums
-
Slight redness
-
No loose teeth
-
No gum recession
-
No deep gum pockets
Signs You May Have Periodontitis
-
Gums pulling away from teeth
-
Chronic bad breath
-
Teeth shifting or separating
-
Pain while chewing
-
Visible gum pockets
-
Loose teeth
-
Gum abscesses
If symptoms go beyond mild bleeding and swelling, you should schedule a dental appointment.
The Stages of Gum Disease
Gum disease progresses gradually. Understanding the stages can help you act early.
1. Healthy Gums
Firm, pink tissue. No bleeding.
2. Gingivitis
Inflamed gums with bleeding, but no bone damage.
3. Early Periodontitis
Minor bone loss begins. Gum pockets deepen slightly.
4. Moderate Periodontitis
Increased bone loss and deeper pocket formation.
5. Advanced Periodontitis
Severe bone destruction, loose teeth, possible tooth loss.
The earlier gum disease is caught, the simpler and less expensive treatment becomes.
Treatment Options: Gingivitis vs Periodontitis
Gingivitis Treatment
Treatment is straightforward:
-
Professional dental cleaning
-
Improved brushing technique
-
Daily flossing
-
Antibacterial mouthwash
-
Regular dental checkups
With consistent care, gums can fully recover within weeks.
Periodontitis Treatment
Treatment is more involved and may include:
-
Scaling and root planing (deep cleaning below gumline)
-
Local or oral antibiotics
-
Laser therapy
-
Gum surgery
-
Bone grafting
-
Ongoing periodontal maintenance visits
While damage cannot be reversed, progression can be stopped.
Why You Should Never Ignore Bleeding Gums
Many people think bleeding gums are normal.
They’re not.
Bleeding is one of the earliest warning signs of inflammation. When ignored, it can slowly progress into periodontitis — often without pain in the early stages.
By the time discomfort appears, damage may already be significant.
Regular dental checkups are essential because gum disease can progress quietly.
Prevention: Protecting Your Gum Health Long-Term
Preventing gingivitis and periodontitis comes down to consistency.
Daily Oral Care
-
Brush twice daily for two minutes
-
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush
-
Floss at least once daily
-
Use fluoride toothpaste
-
Consider antimicrobial mouthwash
Professional Dental Care
-
Dental checkups every six months
-
Professional cleanings
-
Early periodontal evaluations if needed
Lifestyle Adjustments
-
Quit smoking
-
Manage diabetes effectively
-
Eat a balanced, nutrient-rich diet
-
Reduce stress
-
Stay hydrated
Prevention is far easier and far less costly than treating advanced periodontitis.
Long-Term Health Risks of Periodontitis
Gum disease doesn’t only affect your mouth.
Research has linked severe periodontitis to increased risk of:
-
Heart disease
-
Stroke
-
Diabetes complications
-
Respiratory infections
-
Pregnancy complications
Inflammation in the gums can influence inflammation elsewhere in the body.
Your oral health is directly connected to your overall health.
Final Thoughts on Gingivitis vs Periodontitis
When comparing gingivitis vs periodontitis, the difference comes down to severity and permanence.
Gingivitis:
-
Mild inflammation
-
Reversible
-
Limited to gum tissue
Periodontitis:
-
Advanced infection
-
Irreversible bone damage
-
Can lead to tooth loss
The most important takeaway?
Bleeding gums are not normal. They are a warning sign.
Addressing gingivitis early prevents it from progressing into periodontitis potentially saving your smile, your teeth, and your long-term health.
FAQs
Is gingivitis painful?
Usually no. It often causes mild irritation but not severe pain.
Can gingivitis turn into periodontitis?
Yes. If untreated, gingivitis can progress into periodontitis over time.
Can periodontitis be cured?
It cannot be fully reversed, but it can be managed and stabilized with professional treatment.
How long does it take for gingivitis to become periodontitis?
It varies depending on oral hygiene, genetics, and overall health. It can take months or even years.
Is bleeding gums always gingivitis?
Most commonly, yes. However, persistent bleeding should always be evaluated by a dentist.
HEALTH
why does ozdikenosis kill you? A Scientific, Human-Centered Explanation
In recent months, the term ozdikenosis has begun appearing across online forums, comment sections, and social media discussions. As curiosity spreads, so does concern. Many people are asking the same urgent question:
Why does ozdikenosis kill you?
Before diving deeper, it’s important to clarify something essential:
Ozdikenosis is not currently recognized in establish ed medical literature as an officially classified disease.
ed medical literature as an officially classified disease.
It does not appear in standard diagnostic manuals, peer-reviewed research databases, or global public health records.
So why are people searching for it?
When individuals look up “why does ozdikenosis kill you,” they are typically seeking one of three things:
-
An explanation of a rumored or emerging illness
-
Information about a fictional or hypothetical condition
-
Clarity around a misunderstood or misheard medical term
This article takes a scientific and educational approach. Instead of spreading speculation, we’ll explain how real diseases kill the human body, what biological mechanisms lead to fatal outcomes, and how to evaluate health information responsibly in the digital age.
If ozdikenosis were a real condition, what biological processes would cause it to become deadly?
Let’s explore the science behind how serious diseases lead to death.
How Diseases Kill the Human Body: The Core Mechanisms
To understand why any illness becomes fatal, we first need to understand how the body stays alive.
Human survival depends on several interconnected systems working in harmony:
-
Oxygen circulation
-
Brain function
-
Heart activity
-
Organ stability
-
Immune regulation
When a disease severely disrupts one or more of these systems, the body can no longer maintain balance. That breakdown — not just the disease name itself is what leads to death.
Below are the primary biological mechanisms through which illnesses become fatal.
1. Organ Failure
One of the most common pathways to death in serious illness is organ failure.
Major organs include:
-
Heart
-
Lungs
-
Brain
-
Liver
-
Kidneys
Each of these plays a non-negotiable role in keeping you alive.
If a disease damages one of these organs beyond recovery, the body cannot compensate indefinitely.
For example:
-
Respiratory failure prevents oxygen from entering the bloodstream.
-
Heart failure stops blood circulation.
-
Liver failure leads to toxin accumulation in the body.
-
Kidney failure disrupts electrolyte and fluid balance, which can cause cardiac arrest.
If ozdikenosis were a fatal disease, it would likely involve progressive damage to one or more critical organs.
Death rarely happens because of a single symptom. It happens because vital systems collapse.
2. Severe Infection and Sepsis
Another life-threatening pathway is systemic infection.
When harmful bacteria, viruses, or toxins spread throughout the bloodstream, the immune system reacts aggressively. In extreme cases, this can lead to sepsis a dangerous condition where inflammation becomes widespread and uncontrollable.
Sepsis can cause:
-
Extremely low blood pressure
-
Impaired oxygen delivery
-
Multi-organ failure
-
Septic shock
-
Death
Ironically, in sepsis, it is often the body’s own immune response that causes much of the damage.
If ozdikenosis involved infectious spread, uncontrolled inflammation and sepsis could be the mechanism behind fatal outcomes.
3. Oxygen Deprivation (Hypoxia)
Every cell in your body depends on oxygen to produce energy.
Without oxygen:
-
Cells begin to malfunction
-
Tissues deteriorate
-
Organs shut down
The brain is particularly sensitive. Permanent brain damage can begin within minutes of oxygen deprivation.
Diseases that affect:
-
Lung function
-
Blood circulation
-
Hemoglobin levels
-
Airway structure
Can lead to hypoxia, a condition where tissues do not receive enough oxygen.
If ozdikenosis interfered with breathing or oxygen exchange, death could occur through respiratory collapse.
4. Neurological Shutdown
The brain controls:
-
Breathing rhythm
-
Heart rate
-
Blood pressure
-
Consciousness
-
Reflexes
If a disease attacks the central nervous system especially the brainstem it can disrupt automatic life-sustaining functions.
Neurological shutdown may result from:
-
Severe infection
-
Inflammation
-
Stroke
-
Trauma
-
Toxin exposure
When the brain can no longer regulate the body’s core functions, survival becomes impossible without advanced life support.
5. Immune System Overreaction
Sometimes, the immune system becomes the problem.
In certain severe illnesses, the body releases excessive inflammatory chemicals known as cytokines. This overreaction often called a “cytokine storm” can cause widespread tissue damage.
Effects may include:
-
Lung inflammation
-
Organ swelling
-
Blood clotting abnormalities
-
Circulatory collapse
Rather than protecting the body, the immune response begins harming it.
This is one of the reasons some viral infections become deadly.
Hypothetical Progression of a Fatal Disease Like Ozdikenosis
If ozdikenosis were a real progressive illness, it might follow stages similar to other systemic diseases.
Stage 1: Early Symptoms
In early stages, symptoms may appear mild:
-
Fatigue
-
Low grade fever
-
Headaches
-
Muscle weakness
-
Mild discomfort
At this stage, many people might ignore symptoms or assume it’s a minor illness.
Stage 2: Systemic Spread
As the illness progresses, it begins affecting multiple systems:
-
Circulatory function
-
Respiratory efficiency
-
Immune balance
Symptoms intensify:
-
Persistent fever
-
Shortness of breath
-
Chest discomfort
-
Brain fog or confusion
This stage often marks a turning point where medical intervention becomes critical.
Stage 3: Organ Complications
Now the disease interferes with core life systems:
-
Oxygen delivery declines
-
Blood pressure drops
-
Inflammation increases
-
Kidney or liver function deteriorates
Without treatment, organ damage may become irreversible.
Stage 4: Critical Failure
The final stage of many fatal diseases includes:
-
Multi organ failure
-
Septic shock
-
Cardiac arrest
-
Neurological shutdown
This is not unique to any one illness. It is the biological endpoint of severe systemic disruption.
Risk Factors That Increase Fatality
Whether discussing real diseases or hypothetical ones, certain risk factors increase the chance of severe outcomes:
-
Weakened immune system
-
Chronic medical conditions
-
Advanced age
-
Delayed treatment
-
Poor nutrition
-
Limited healthcare access
Early detection and treatment often make the difference between recovery and fatal progression.
Why Accurate Medical Information Matters
Because ozdikenosis is not recognized in medical literature, it is essential to avoid spreading misinformation.
In today’s digital environment, unfamiliar health terms can go viral quickly through:
-
Social media posts
-
Online discussion threads
-
Short form video platforms
-
Unverified blogs
Fear spreads faster than facts.
Before accepting any alarming health claim, verify information through:
-
Licensed medical professionals
-
Peer-reviewed research
-
Government health agencies
-
Accredited hospitals
Misinformation can cause unnecessary panic — or worse, delay treatment for real illnesses.
The Psychological Side of Searching “Why Does Ozdikenosis Kill You?”
Health related anxiety is common in the internet age.
When someone searches for a fatal disease, it often reflects:
-
Fear about unexplained symptoms
-
Exposure to viral content
-
Concern triggered by social media
-
Health anxiety
If you find yourself worrying persistently about unknown diseases, consider speaking with a healthcare provider rather than relying solely on online discussions.
Reassurance from a qualified professional is far more reliable than speculation.
How Real Diseases Are Diagnosed
Legitimate medical conditions are identified through structured evaluation:
-
Clinical examination
-
Symptom history
-
Laboratory testing
-
Imaging (X-rays, MRI, CT scans)
-
Biopsy (when necessary)
-
Peer reviewed classification
If a disease lacks scientific documentation, it should be approached cautiously.
Medicine relies on evidence, not viral trends.
Preventing Severe Illness in General
While ozdikenosis is not medically recognized, preventing severe disease overall involves strong foundational health habits:
-
Routine medical checkups
-
Vaccinations when appropriate
-
Balanced nutrition
-
Regular physical activity
-
Adequate sleep
-
Stress management
-
Avoiding tobacco
-
Limiting alcohol consumption
Strengthening your overall health reduces vulnerability to many serious conditions.
Could Ozdikenosis Be a Misunderstood Term?
Sometimes unfamiliar medical-sounding words originate from:
-
Misspellings
-
Fictional stories
-
Online hoaxes
-
Viral jokes
-
Misinterpretation of real diseases
Before assuming a new disease is real, check:
-
Recognized medical databases
-
Public health websites
-
Academic research publications
Critical thinking protects both your mental and physical well-being.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Regardless of terminology, seek urgent care if you experience:
-
Severe chest pain
-
Difficulty breathing
-
Sudden confusion
-
High persistent fever
-
Fainting
-
Uncontrolled bleeding
These symptoms require immediate evaluation — regardless of what you call the illness.
Why Fear Based Health Content Spreads So Fast
Content about deadly diseases spreads quickly because it triggers:
-
Survival instincts
-
Emotional reactions
-
Curiosity
-
Social sharing behavior
But viral popularity does not equal medical validity.
Being informed not alarmed is the healthier approach.
Final Thoughts: Why Does Ozdikenosis Kill You?
Based on current scientific evidence, ozdikenosis is not a recognized medical condition.
There is no verified medical explanation for how it kills — because it does not appear in established clinical literature.
However, understanding how real diseases become fatal provides context.
Diseases kill by:
-
Causing organ failure
-
Disrupting oxygen circulation
-
Triggering systemic infection
-
Damaging the nervous system
-
Creating uncontrolled inflammation
If you encounter alarming health terms online, verify them through reliable sources before assuming danger.
Knowledge reduces fear.
Critical thinking prevents misinformation.
And responsible health decisions protect lives.
FAQs
1. Is ozdikenosis a real disease?
There is no verified medical evidence that ozdikenosis exists as a recognized illness.
2. Why are people searching for ozdikenosis?
It may be trending due to misinformation, fictional references, or misunderstandings of medical terminology.
3. How do real diseases kill people?
Through organ failure, infection, oxygen deprivation, neurological damage, or systemic inflammation.
4. Should I be worried about ozdikenosis?
There is currently no scientific basis for concern.
5. What should I do if I feel sick?
Consult a licensed healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
HEALTH
5 Ways Orthodontics Can Positively Impact Speech And Chewing
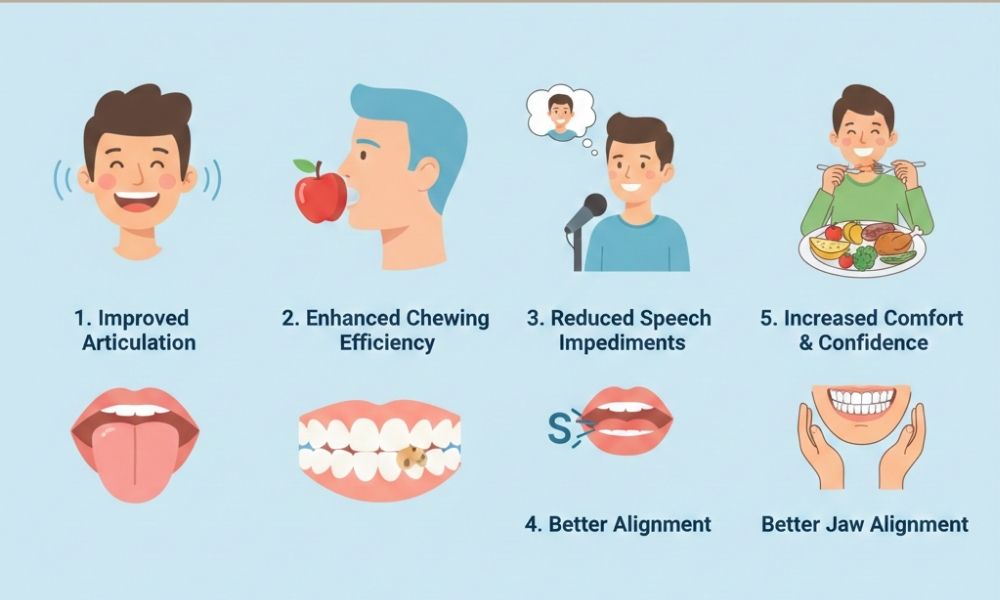
Speech and chewing affect how you connect with people and how you nourish your body. When teeth or jaws do not line up, simple tasks like saying certain sounds or chewing solid food can feel exhausting. Orthodontic care can correct these problems. It can guide teeth into better positions. It can also support jaw alignment. As a result, you may speak with more clarity. You may chew with less strain. You may feel less tension in your face and neck. Many people notice these changes during treatment, not only at the end. If you struggle with slurred words, mouth breathing, or slow chewing, targeted tooth movement can help. This is true for children, teens, and adults. Local options, such as braces in La Quinta, Ca, can address both comfort and function. The next five points explain how orthodontics can reshape speech and chewing in practical, everyday ways.
1. Straightening Teeth To Support Clearer Speech
Speech sounds depend on where your tongue, lips, and teeth meet. When front teeth lean forward, crowd, or leave a large gap, sounds like S, Z, T, and D can come out fuzzy. You may notice a lisp or air leaking between teeth.
Orthodontic treatment moves teeth into a more even row. This gives your tongue a steady surface. It also reduces extra spaces that let air escape. Over time, this can support clearer words and stronger sound control.
You may see changes in three stages.
- Early stage. Your mouth adjusts to braces or aligners. Speech may feel awkward for a short time.
- Middle stage. Teeth shift into healthier positions. Sounds often grow sharper.
- Final stage. Tongue and lips adapt to the new bite. Speech can feel steady and natural.
The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders explains how the structure in the mouth shapes speech sounds.
2. Improving Bite Alignment For Safer, Stronger Chewing
Chewing depends on how your upper and lower teeth meet. When you have an overbite, underbite, open bite, or crossbite, your teeth may grind on the wrong spots. This can make chewing slow, uneven, or painful.
Orthodontic care can guide your bite into a pattern that spreads chewing forces across more teeth. This can reduce wear and lower the risk of cracked teeth. It can also help you break food into smaller pieces before you swallow.
Here is a simple comparison of common bite problems and how orthodontics can help.
| Type of bite problem | Common chewing effect | Possible orthodontic benefit
|
|---|---|---|
| Overbite | Front teeth carry too much pressure during biting | Moves pressure toward back teeth for stronger chewing |
| Underbite | Front teeth may not cut food well | Improves overlap of front teeth so they can slice food |
| Open bite | Front teeth do not touch. Chewing relies on back teeth only | Closes the gap so front teeth can help bite through food |
| Crossbite | Teeth hit in uneven ways. Jaw may shift during chewing | Lines up teeth to reduce stress on jaw joints |
The National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research notes that a healthy bite supports steady chewing and lowers the risk of tooth damage.
3. Supporting Jaw Joints And Reducing Strain
When teeth do not meet well, your jaw joints work harder to close your mouth. You may feel clicks, pops, or soreness near your ears or cheeks. You may also clench or grind at night without knowing it.
Orthodontic treatment can help the jaw move along a more natural path. When teeth fit together in a stable way, muscles around your face and neck do not need to pull as hard. This can reduce strain and protect the joints.
You may notice:
- Less jaw fatigue after meals
- Fewer headaches tied to chewing
- Less clenching or grinding during stressful days
For many families, this change shifts daily life. Mealtimes can feel calmer. Children may complain less about jaw pain. Adults may feel more willing to eat crunchy or chewy foods again.
4. Encouraging Healthier Breathing And Tongue Habits
Mouth breathing and tongue thrust are common in children and teens. Crooked teeth or a narrow arch can make nasal breathing harder. They can also give the tongue less room. Over time, these habits can hurt both speech and chewing.
Orthodontic care can widen arches and create more space for the tongue. It can help close open bites that often link to tongue thrust. As teeth move, you may find it easier to keep your lips closed and breathe through your nose.
Healthier breathing and tongue habits can:
- Support clearer sounds, especially S and Z
- Help lips seal around utensils and cups
- Reduce choking risk during fast meals
In some cases, your orthodontist may work with a speech therapist. Together, they can guide new tongue patterns while your teeth move. This team approach can give your family more lasting results.
5. Building Confidence In Eating And Speaking Around Others
Teeth alignment affects more than function. It shapes how you feel when you speak or chew in front of others. If you worry that food will slip from your teeth or that your words will sound unclear, you may stay quiet. You may eat less in public. You may avoid social events.
Orthodontic treatment can ease these fears. As speech grows clearer and chewing feels safer, you may feel more at ease. You may speak up in class or at work. You may sit through a family meal without fear of pain or embarrassment.
Families often report three common shifts.
- Children answer more questions out loud in school.
- Teens feel less nervous about eating with peers.
- Adults join more social meals and work events.
This change does not come from looks alone. It comes from trust in your bite and your voice. That trust can lower stress for the whole household.
Taking The Next Step For Your Family
If you notice speech struggles, slow chewing, or jaw pain, an orthodontic check can bring clarity. A short exam and simple images can show how your teeth and jaws line up. You can then talk about choices that fit your age, health, and daily life.
You do not need to wait for severe problems. Early action can protect teeth, ease strain, and support clear speech for years. With careful planning, orthodontic care can help your family eat, speak, and smile with steady confidence.
-

 CELEBRITY1 year ago
CELEBRITY1 year agoLinda Susan Agar: A Visionary Leader Shaping the Future of the Technology Industry 2024
-

 CRYPTO1 year ago
CRYPTO1 year agoeCrypto1.com Crypto Wallets: The Ultimate Guide to Secure and Efficient Cryptocurrency Storage 2025
-

 CELEBRITY1 year ago
CELEBRITY1 year agoThe Viral “Emiru Handbra” Moment: How It Became a Stunning Social Media Sensation in 2024
-

 CELEBRITY1 year ago
CELEBRITY1 year agoThe Life and Legacy of Harlow Andrus: A Journey of Heritage and Inspiration 2024
-

 FASHION1 year ago
FASHION1 year agoMcKinzie Valdez: Journey from Social Media Star to Entrepreneur 2024
-

 CELEBRITY1 year ago
CELEBRITY1 year agoMatt Danzeisen: The Quiet Yet Powerful Figure Behind Peter Thiel’s Success 2024
-

 CELEBRITY1 year ago
CELEBRITY1 year agoWho is Josie Lynn Shalhoub’s? Tony Shalhoub’s Daughter
-

 CELEBRITY1 year ago
CELEBRITY1 year agoDavid Nehdar: The Private Life and Success of Lacey Chabert’s Husband 2025